Pull from GitHub
1. Pull from GitHub
Pulling to Keep up-to-date with Changes
When working as a team on a project, it is important that everyone stays up to date.
Any time you start working on a project, you should get the most recent changes to your local copy.
With Git, you can do that with pull.
pull is a combination of 2 different commands:
fetchmerge
Let's take a closer look into how fetch, merge, and pull works.
Git Fetch
fetch gets all the change history of a tracked branch/repo.
So, on your local Git, fetch updates to see what has changed on GitHub:
Example
git fetch origin
remote: Enumerating objects: 5, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), 733 bytes | 3.00 KiB/s, done.
From https://github.com/w3schools-test/hello-world
e0b6038..d29d69f master -> origin/masterNow that we have the recent changes, we can check our status:
Example
git status
On branch master
Your branch is behind 'origin/master' by 1 commit, and can be fast-forwarded.
(use "git pull" to update your local branch)
nothing to commit, working tree cleanWe are behind the origin/master by 1 commit. That should be the updated README.md, but lets double check by viewing the log:
Example
git log origin/master
commit d29d69ffe2ee9e6df6fa0d313bb0592b50f3b853 (origin/master)
Author: w3schools-test <77673807+w3schools-test@users.noreply.github.com>
Date: Fri Mar 26 14:59:14 2021 +0100
Updated README.md with a line about GitHub
commit e0b6038b1345e50aca8885d8fd322fc0e5765c3b (HEAD -> master)
Merge: dfa79db 1f1584e
Author: w3schools-test
Date: Fri Mar 26 12:42:56 2021 +0100
merged with hello-world-images after fixing conflicts
...
...That looks as expected, but we can also verify by showing the differences between our local master and origin/master:
Example
git diff origin/master
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 23a0122..a980c39 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -2,6 +2,4 @@
Hello World repository for Git tutorial
This is an example repository for the Git tutoial on https://www.w3schools.com
-This repository is built step by step in the tutorial.
-
-It now includes steps for GitHub
+This repository is built step by step in the tutorial.
\ No newline at end of fileThat looks precisely as expected! Now we can safely merge.
Git Merge
merge combines the current branch, with a specified branch.
We have confirmed that the updates are as expected, and we can merge our current branch (master) with origin/master:
Example
git merge origin/master
Updating e0b6038..d29d69f
Fast-forward
README.md | 4 +++-
1 file changed, 3 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)Check our status again to confirm we are up to date:
Example
git status
On branch master
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/master'.
nothing to commit, working tree cleanThere! Your local git is up to date!
Git Pull
But what if you just want to update your local repository, without going through all those steps?
pull is a combination of fetch and merge. It is used to pull all changes from a remote repository into the branch you are working on.
Make another change to the Readme.md file on GitHub.
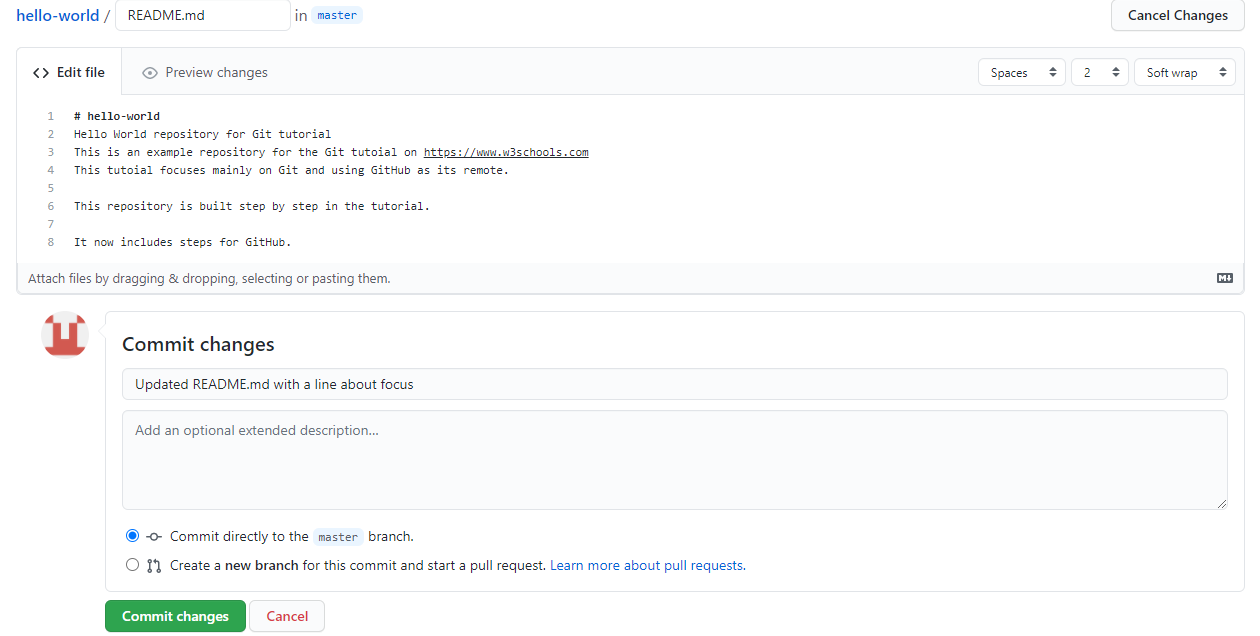
Use pull to update our local Git:
Example
git pull origin
remote: Enumerating objects: 5, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (5/5), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done.
remote: Total 3 (delta 1), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), 794 bytes | 1024 bytes/s, done.
From https://github.com/w3schools-test/hello-world
a7cdd4b..ab6b4ed master -> origin/master
Updating a7cdd4b..ab6b4ed
Fast-forward
README.md | 2 ++
1 file changed, 2 insertions(+)That is how you keep your local Git up to date from a remote repository. In the next chapter, we will look closer at how push works on GitHub.